Many plastic products used in our daily life are fabricated using injection molding process. It involves the injection of plastic material into a mold. The key advantage of this process is the ability to manufacture products in large scale at low cost. This process is also suitable for a wide variety of products varying in size, complexity, and application.
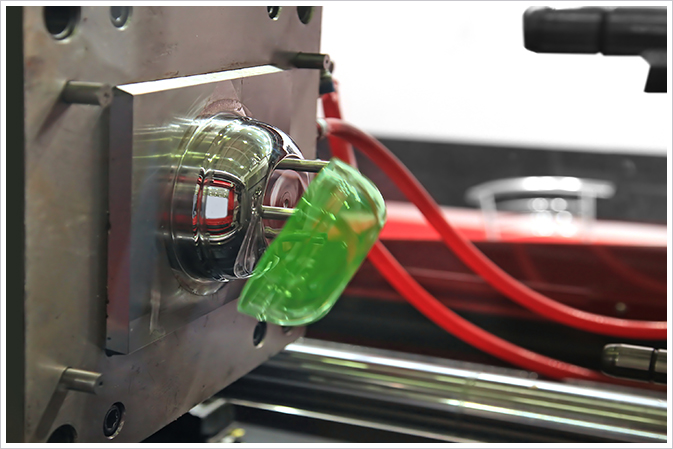
Mold designing is the most important factor in determining the quality of the finished product. Molding conditions such as the injection speed, barrel temperature, mold temperature, and the quality of the mold are also kept into consideration. These can considerably change the appearance, dimensions, and other properties of the molded products.
Many thin-walled parts for various applications are produced using injection molding process. These parts are used in household appliances, automotive dashboards, and consumer electronics. Several other items such as plastic toys, medical devices, including syringes are also produced using injection molding process.
The injection molding process requires the use of an injection molding machine, raw material (usually plastic), and a mold. The material is injected in the machine where it is heated and pushed into the mold. It then cools and takes the shape of the mold. The steps involved in this process are described below in length.
Steps in Injection Molding Process
The process cycle for injection molding is very short, using high pressure injection of the material into a mold, where it is shaped. Complete process usually takes 2 seconds to 2 minutes, divided into various stages. These are: clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, mold opening, and ejection.
Clamping – The first step starts with the holding of the mold tool together under pressure. This is done by the clamping unit which securely closes the two halves of the mold against the pressure of the melted materials being injected, avoiding the resin from spilling out.
When attached to the mold machine, one half is left free to slide. When the material is injected, the clamping unit pushes the halves together allowing them to be held tight. The moving and fixed platens of the injection molding machine work on hydraulic powers. Time taken to close and clamp the mold is dependent upon the machine. Larger machines take longer.
There are two types of clamping methods: toggle and straight-hydraulic type. The first is a conventional system which uses link mechanism. Immediate drawback here is lack of perfection. Slippage can cause damage to the molds created by this method. The second method is suitable for high tonnage machines providing molding stability and minimal inconsistencies.
Injection – The function of this section is to inject the material into the mold. The material, which is in the pallet form, is injected into the barrel of the injection molding machine. As the barrel is surrounded by heat, the pallets melt.
The amount of material that is injected is called shot. Due to the complexity and changing flow of the molten material, it is difficult to calculate the exact injection time. However, the volume of the material and injection pressure & power do indicate this duration.
Dwelling – After the molten material is injected into the mold, pressure is applied to ensure all cavities are filled. This pressure pushes the pallets toward the mold, where it takes the shape. Pressure and the rate of injection can be controlled by the hydraulic system of the machine.
Cooling – The molten plastic inside the mold is allowed to cool and solidify. It takes the shape of the mold and remains intact until the part is cooled. The part may shrink a little during this process. The cooling time can be calculated from the thickness and the thermodynamic properties of the material.
Mold opening – As soon as the cooling time is over, the mold opens from the sliding section, pushing out the created part.
Ejection – The last step is to remove the cooled part from the mold. Force is applied here because the part gets stuck to the mold when cooled.
Once the process is complete, finishing touch is definitely required.
Advantages of Injection Molding Process
- Injection molding can manufacture good number of parts per hour
- Consistency in the product
- Highly accurate
- Allows the manufacturing of complex products in different shapes and designs
- Fast production
- Wide range of plastic materials can be used
- Can also be used to manufacture very small parts
- Complete flexibility with the design
- Mass production is possible
- Waste can be reused as most plastics recycle
- Color and material flexibility
- High tolerances are repeatable
- In future, reproduction of the manufactured items is also possible
- Reduced work load
- Cost effective as this is an automated process. Hence, labor cost is low.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding Process
- Initial cost to prepare the tool for injection molding is high
- Designs must be created before any process begins which can delay the production
- Part design restriction
- Molds are made of metal and hence, difficult to modify
- Can be costly if used for less number of productions

